Understand How Assessments per Heartbeat Work
One of the core operations of Monnit Sensors is the Aware State. The Aware State is based on a few configurations which allow for three distinct characteristics:
- Low power operation (preservation of battery life)
- Edge processing at sensor level
- Deliberate sizing of datasets (not too many, not too few data points)
Using the Aware State and Assessment per Heartbeat configurations, you can enjoy these benefits. The Aware State allows a sensor to monitor particular conditions like temperature or vibration and report data when the preconfigured settings for those conditions are met. In other words, it enables your sensor to report data when a specific condition occurs. This happens without bombarding you with data. The sensor watches for the condition quietly in the background. Aware State and Assessments per Heartbeat are the sensor settings configurations used to accomplish this remote monitoring process.
Assessments per Heartbeat
Assessments per Heartbeat is a configuration found on most Interval Sensor Settings. This setting tells the sensor how many times per Heartbeat Interval it should take a sample to see if the current condition breaches the configured Aware State Threshold. Suppose the reading taken on the Assessment breaches the configured Aware State Threshold. The sensor will immediately wake its radio and transmit the reading to iMonnit (if configured to trigger a Heartbeat on Aware message). When your sensor detects a condition outside of the Aware State Threshold, the data will be immediately visible in iMonnit.
If the sensor doesn’t detect a breach in the Aware State Threshold, the sensor goes back to sleep and discards the sample taken during that Assessment.
Note: If the reading doesn’t breach the Aware State Threshold, the sensor discards the reading, and you can’t retrieve the data.
Example
Consider a sensor configured with 20-minute Heartbeats and Assessments per Heartbeat set to 10. With this configuration, the sensor checks 10 times during the 20-minute Heartbeat (every two minutes) whether the condition is outside of the Aware State Threshold. This means the sensor checks on this condition once every two minutes for a breach in the Aware State Threshold. If the assessment detects a threshold breach, the reading is transmitted immediately, allowing for prompt notification of the condition within one minute.
In addition, the sensor starts checking on the condition during the Aware State Heartbeat Interval. Users often configure the Aware State Heartbeat Interval Assessments to be more frequent than the standard Heartbeat to watch a current condition.
Configuring Assessments per Heartbeat
The default configuration for Assessments per Heartbeat is one. This default configuration means the sensor only reports readings on its scheduled Heartbeat interval. Suppose you want the sensor to check against the Aware State Threshold and report a reading before that scheduled Heartbeat. In that case, you must change the Assessments per Heartbeat configuration to allow the sensor to check the condition with the desired frequency.
The maximum value you can configure for Assessments per Heartbeat is 250. However, the most frequently any sensor can execute an Assessment is once per second. It is worth noting that this can significantly affect battery life. A single Assessment uses about 30% as much battery life for most sensor types as a single Heartbeat.
To configure Assessments per Heartbeat:
- Log into iMonnit.
- Click Sensors in the main navigation menu.
- Select the sensor you wish to configure.
- Select the Settings tab (gear icon).
- Find the field for Assessments per Heartbeat.
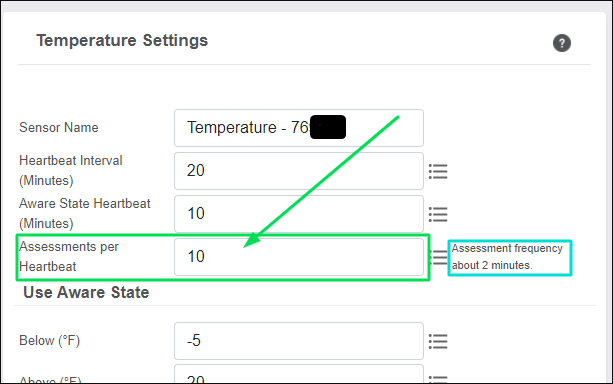
- Enter the number of Assessments you want the sensor to take per Heartbeat (250 maximum up to once per second on most sensors). We suggest that the number of Assessments is a value divisible by the Heartbeat.
Select Save.
When the sensor checks in again, it should accept the configuration.
To configure Assessments per Heartbeat, you must have an active iMonnit Premiere subscription.
Aware State Threshold
As mentioned above, the Aware State Threshold configuration is directly related to the Assessments per Heartbeat. For your sensor to report a particular condition, you must enter the configuration for the condition you wish to monitor. This means you need to enter your sensor’s Aware State Threshold configuration. In most sensors, this is a two-pole threshold. You can configure a lower and upper limit. If the sensor reads below or above these values on an Assessment, the Aware reading will be transmitted immediately.
By default, the Aware State range includes all possible values. Therefore you must configure the Aware State Threshold for the desired sensor.
To configure Assessments per Heartbeat:
- Log into iMonnit.
- Click Sensors in the main navigation menu.
- Select the sensor you wish to configure.
- Select the Settings tab (gear icon).
- Identify the Aware State Threshold configuration for your sensor type.
- Enter the desired Aware State Threshold configuration.
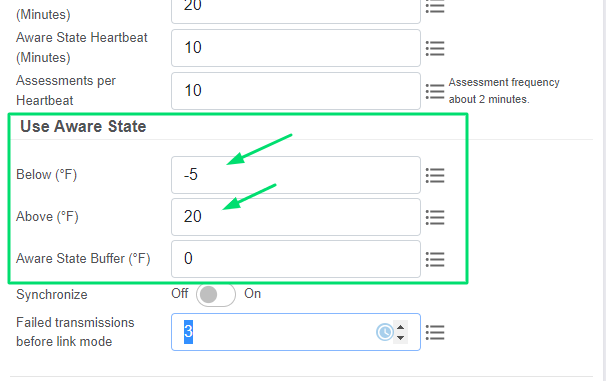
- Select Save. When the sensor checks in again, it should accept the configuration.
Note: the exact name and interface of this configuration may differ between sensor types.
In the above example, the sensor will check in every 20 minutes (Heartbeat set to 20), conduct Assessments every two minutes (Assessments set to 10), check in for a temperature below -5°F (Aware State Threshold Below) or above 20°F (Aware State Threshold Above). If, during one of the Assessments, the sensor detects a temperature outside of the threshold, it transmits the reading immediately. It starts checking in every 10 minutes (Aware State Heartbeat) and conducting Assessments every one minute (Assessments).
Once the sensor detects a reading that is back in normal range within the threshold, it reports that to the gateway. Although, since it is not an Aware State message, the gateway will wait until the gateway’s scheduled Heartbeat to deliver that data to iMonnit.