Using an Ethernet Gateway 4 on a Private Modbus TCP or SNMP Network
The ALTA Ethernet Gateway 4 offers Modbus Transmission Control Protocol (TCP) and Simple Network Management Protocol (SNMP) Interfaces which you can poll to receive sensor data from Modbus TCP or SNMP networks. These interfaces are disabled by default but can be enabled through iMonnit Software or the gateway’s local configuration page (HTTP Interface) when a static IP address is configured. The Default Interface (iMonnit Online) is always enabled. It can be disabled if operating the gateway on a private network on which Monnit Software isn’t being used (iMonnit Online, iMonnit Enterprise, iMonnit Express, or Monnit MINE). There are special considerations when enabling these interfaces when the gateway cannot communicate with Monnit software. This article will provide insight into these considerations and steps for operating your gateway with this configuration.
Disabling the Gateway’s Default Server Interface
Note: The gateway’s firmware should always be updated before disabling the gateway’s Default Interface to ensure the gateway’s most up-to-date interface operation.
For the gateway to continue to receive sensor data and respond to polling on the Modbus TCP/SNMP Interface while the gateway is not sending data to Monnit Software, the Default Interface must be disabled. You may find that you’re not receiving sensor data or that your gateway stops responding to polling on the Modbus TCP/SNMP Interface intermittently if there is no connection to Monnit Software, but you haven’t disabled the Default Interface.
As mentioned in this article, you will need to unlock your gateway to disable the Default Server Interface. If the gateway is not unlocked, you won’t see the option to disable this interface. If this interface is left active while operating on a private network and the gateway can’t reach a Monnit server, the gateway will continually reach out to iMonnit unsuccessfully, and the sensor network will go inactive. This will be demonstrated by sensor data not being updated in the device’s sensor registers, and the sensor LED (top LED) will go dark.
Once the gateway is unlocked, you can disable the Default Server Interface by accessing the gateway’s local configuration page (HTTP Interface) through a browser, clicking the Data Interfaces tab, and selecting Default Server Configuration, turning it off, and clicking Save Changes. When the gateway reboots, it will no longer attempt to report data to Monnit Software.
Data Interfaces Offered by the Gateway
The Ethernet Gateway 4 offers five data interfaces.
- Default Server Interface (iMonnit Online, iMonnit Enterprise, iMonnit Express, and Monnit MINE)
- Modbus TCP
- SNMP
- SNTP (Simple Time Network Protocol)
- HTTP Interface (local configuration page)
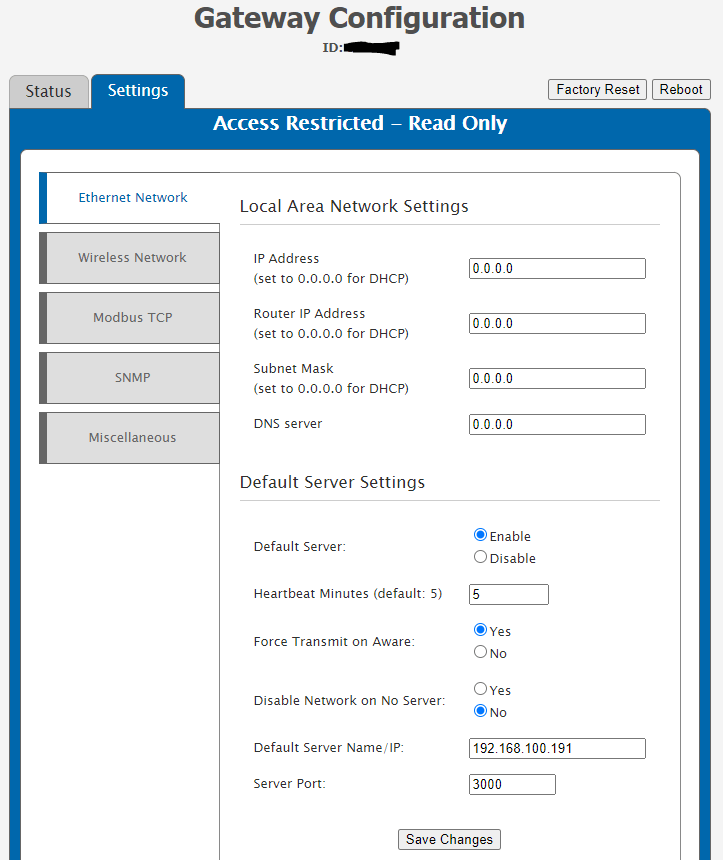
Default Server Interface
This is the interface on which the gateway sends data to iMonnit. With the default configuration, the gateway’s Default Server Interface is enabled to communicate with iMonnit over the Internet on TCP port 3000. The gateway can be unlocked and pointed to communicate using the Default Interface to local Monnit Software such as iMonnit Enterprise, Express, or MINE. It is important to consider that the gateway may need to first communicate with the iMonnit online portal to be unlocked and pointed. In most cases, the gateway will first need to connect to a network that allows an Internet connection over TCP port 3000 to be configured to operate with a local version of iMonnit Software. In any case, the Default Interface represents a connection to Monnit Software.
Modbus TCP Interface
The Modbus TCP Interface is a read-only interface to poll the gateway to provide gateway and sensor data on an Ethernet Modbus TCP network. Modbus TCP is a non-streaming data interface standard. This means data must be requested for it to be received. The Modbus TCP Interface will store all data values in 16-bit registers. You must enable a static IP address on the gateway to poll the data. Activate this interface through Monnit Software or the local configuration page (HTTP Interface). The Modbus TCP Interface doesn’t support Server ID configuration.
SNMP Interface
The Ethernet Gateway 4 includes an SNMP V1 Interface, which allows polling the gateway for sensor data using the SNMP protocol. By default, the community string for the gateway is “public,” which can be configured using the local configuration page (HTTP Interface). The gateway supports the Walk command, and the management information base (MIB) for the SNMP Interface can be downloaded at the link below. There is also an Internet MIB to decode the SNMP data. In addition to the main SNMP Interface, the gateway also offers the ability to send SNMP Traps to a specific endpoint. This can be enabled through Monnit Software or the local configuration page.
https://monnit.azureedge.net/content/downloads/MONNIT-EGW4.mib
SNTP Interface
Note: If you disable the Default Server Interface, you must configure the SNTP Interface in gateways with firmware before version 1.0.5.5. In earlier versions of the firmware, your gateway’s sensor network will be disabled unless the status “On and Synced” is in the gateway’s local configuration Status page for SNTP. If the status shows only “On,” the gateway can’t retrieve time from the SNTP server. In this case, the sensor network LED (top LED) will also not illuminate. You will either need to update the gateway’s firmware through the iMonnit online portal to version 1.0.5.5 or later (which does not require SNTP when the Default Server Interface is disabled) or enable SNTP on the gateway and point to a valid SNTP server on the network.
An SNTP Interface is included on the Ethernet Gateway 4. SNTP is a synchronized computer clock on a network. An SNTP server can be set up on the same LAN as the gateway, such as on a router or a computer (Windows includes an SNTP service). The gateway should be configured to retrieve time from only trusted servers, such as those maintained by your ISP. Incorrect time can affect the delivery of sensor traffic. If the Default Interface is active, it will be utilized for time synchronization in ordinary operations. Therefore, SNTP will be used as a backup.
HTTP Interface (local configuration page)
The gateway also offers an HTTP Interface that allows you to access the gateway’s local configuration page. Details on how to access this page can be found at Ethernet Gateway 4 - Accessing local configuration page (HTTP Interface) Locally
Configure Sensors
The Default Server Interface is the single interface that offers the capability of configuring sensors. Since this is the only interface by which sensor configuration can be delivered to sensors, some form of Monnit Software is required to change sensor configurations from their default settings. The most commonly changed sensor configurations are the sensor’s Heartbeat and Aware State Heartbeat. By default, these are set to 120 minutes. If you want to operate your sensors with a more frequent Heartbeat than 120 minutes (or any other configuration changes) while your gateway is operating on a private network with no connection to Monnit Software (Default Server Interface disabled), the sensor needs to be configured using Monnit Software before disabling the Default Interface.
It is also important to understand that sensors perform a handshake in which they communicate 10 times 30 seconds apart when the first connect, then return to their preconfigured Heartbeat. This can lead to the impression that the sensor loses connection shortly after powerup, though it is expected behavior.
Note: There is no way to configure sensors using the gateway’s local configuration page (HTTP Interface).
If you wish to modify sensor configurations in the future, the Default Interface must be enabled, and the sensor needs to be configured using Monnit Software. For customers that do not have the option of connecting the gateway to the Internet, you may consider running a local version of Monnit Software such as Enterprise or developing software using the MINE SDK.
This also means that your sensor Heartbeat configuration will be limited by the version of Monnit Software you use to configure the sensors. Currently, the minimum Heartbeat for a sensor using iMonnit online is one minute (if you purchase and apply iMonnit HX Credits) or 10 minutes with a standard iMonnit Premiere license. The local versions of Monnit Software (Enterprise, Express, MINE) allow for 1-second minimum Heartbeats for most sensors.
Conclusion
The interaction between the Default Server Interface, Modbus TCP/SNMP interfaces, unlock status, SNTP, and sensor configurations are critical to successfully implementing a gateway on a private Modbus TCP or SNMP network. This article should be useful in understanding these details, but if you have further inquiries, feel free to contact Monnit Support.